May 26, 2022
Normal tantrums versus abnormal tantrums

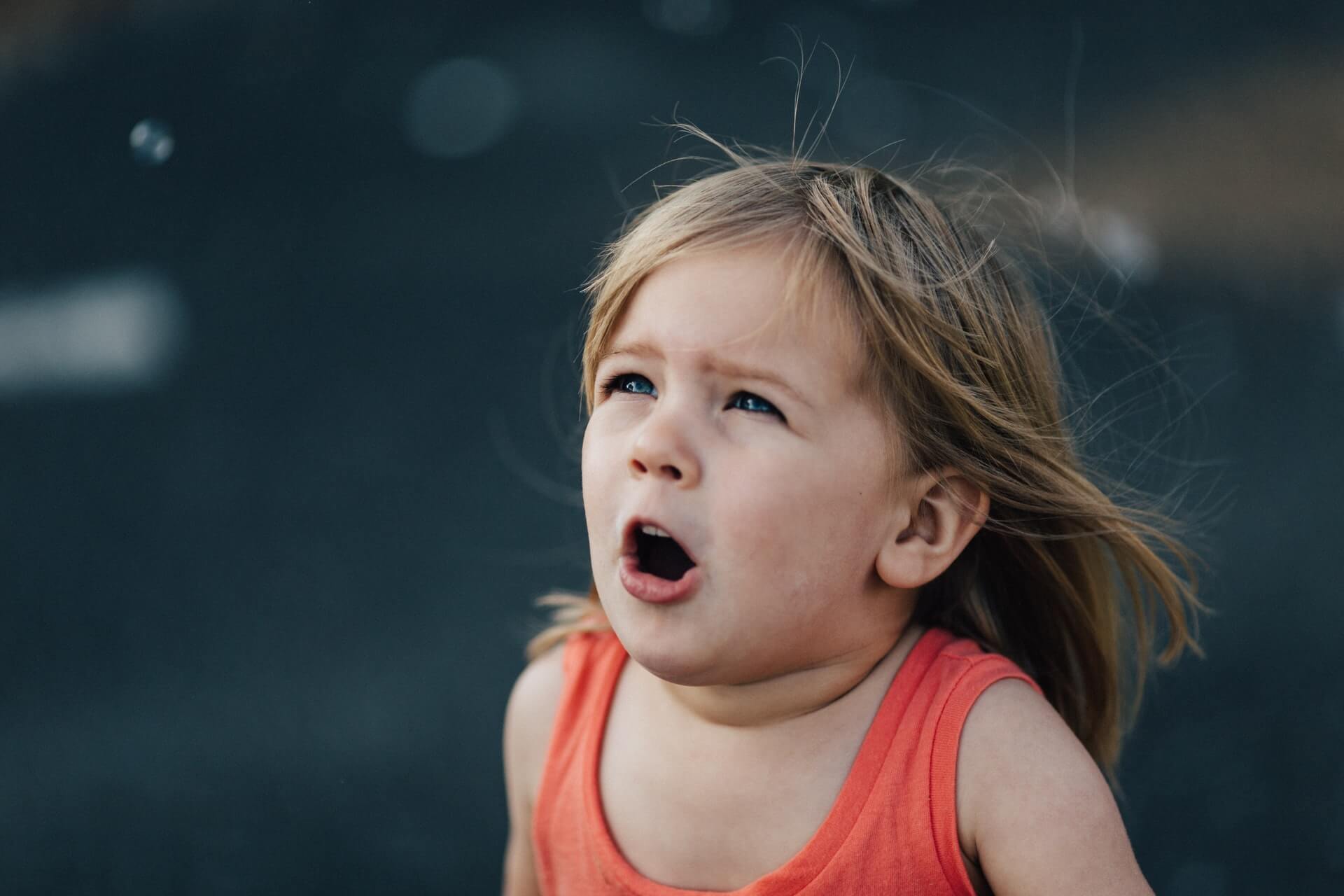
What Child’s Temper More Than A Tantrum?
About Child’s Temper Parents have asked us what differentiates a developmentally normal tantrum from something to be concerned about and address. Some research in this area has identified key differences between good old-fashioned tantrums and signs that a child may be dealing with a larger problem, such as sleep deprivation, illness, anxiety, depression, or other mood or behavioural disorders.
Eighty per cent of all preschoolers have tantrums from time to time, but daily tantrums are unusual. Normative tantrums are frequently triggered by obvious cues such as frustration, jealousy, or exhaustion. Tantrums that are concerning are more likely to occur without a clear trigger or “out of the blue.”
Normal tantrum components
Here are some key elements of tantrums that have been found to differentiate children with disruptive, depressive, or anxiety symptoms from their healthy peers in preschoolers:
At what age do temper tantrums stop?
- Tantrums’ duration. Healthy preschoolers have tantrums that last less than 25 minutes, whereas children who have tantrums that last longer than 25 minutes are more likely to have other behavioural or mood issues.
- Tantrum frequency. If tantrums occur more frequently, it may be an indication of a more serious behavioural or mood problem:
- Quality of the tantrum. The following are all indicators of potentially serious behavioural or mood concerns if they occur during the tantrum:
- The inability of the child to calm down without the assistance of a caregiver
- Display of aggression towards other people or objects more than 50 per cent of the time during tantrums
- Attempt to hurt themselves during the tantrum, which may indicate the presence of depression
How Do You Deal With An Angry Disrespectful Child?
If your child’s tantrums are indicating a larger problem, it is critical that you seek help right away. Childhood development psychologists or psychiatrists are a good place to start. They can assist in evaluating your child in order to identify underlying issues and develop a treatment plan.
When temper tantrums occur frequently and with severity, it is very distressing for parents and children, as well as disruptive to home and school. There are treatments that can help improve children’s functioning, the parent-child relationship, and school performance. Getting your child the help he or she requires can help prevent larger problems from developing and can teach him or her important skills for managing emotions as a child and as an adult.
References
- A.C. Belden, N.R. Thomson, and J.L. Luby (2008). Temper tantrums in healthy versus depressed and disruptive preschoolers: Defining tantrum behaviours associated with clinical problems. Journal of Pediatrics, 152, pp. 117-122.
View more posts tagged, parent
This page is based on professional advice from reputable medical and government organizations, such as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. This page’s material should not be used in place of professional medical advice. For a complete diagnosis and treatment, always seek the advice of a medical expert.











Leave a Reply
View Comments